Losing hair can be distressing for men and for women. Especially for those experiencing androgenetic alopecia, commonly known as male or female pattern baldness. While hair loss treatments abound, many can come with unwanted side effects or have limited efficacy.
But what if we told you there’s a medication that’s been found to help reduce hair loss and improve hair density, particularly in women? Spironolactone, normally used to treat high blood pressure and heart failure is increasingly used off-label for hair loss.
Spironolactone is the most widely used antiandrogen for female pattern hair loss in the United States. In other countries such as Australia, spironolactone has been used for well over 20 years, particularly in women who have not yet had the menopause. Some research suggests that spironolactone will become a frequent therapy for people who do not respond well to minoxidil.1
In this article, we’ll explore what spironolactone is, how it works, its effectiveness for hair loss, and everything else you need to know before considering this treatment option.
What is spironolactone?
Spironolactone is a medication that belongs to the class of drugs known as aldosterone antagonists.2 Traditionally, it is used as a treatment for high blood pressure and heart failure. How? Well, spironolactone works by blocking (antagonizing) the effects of aldosterone. Aldosterone is a hormone produced by the adrenal glands which regulates our blood pressure by affecting the balance of sodium and water in the body. Normally, aldosterone causes the body to retain sodium and water but by blocking aldosterone, spironolactone causes the kidneys to excrete excess salt and water, which can reduce blood pressure and improve heart function in those with heart failure.
Spironolactone for hair loss – how does it work?
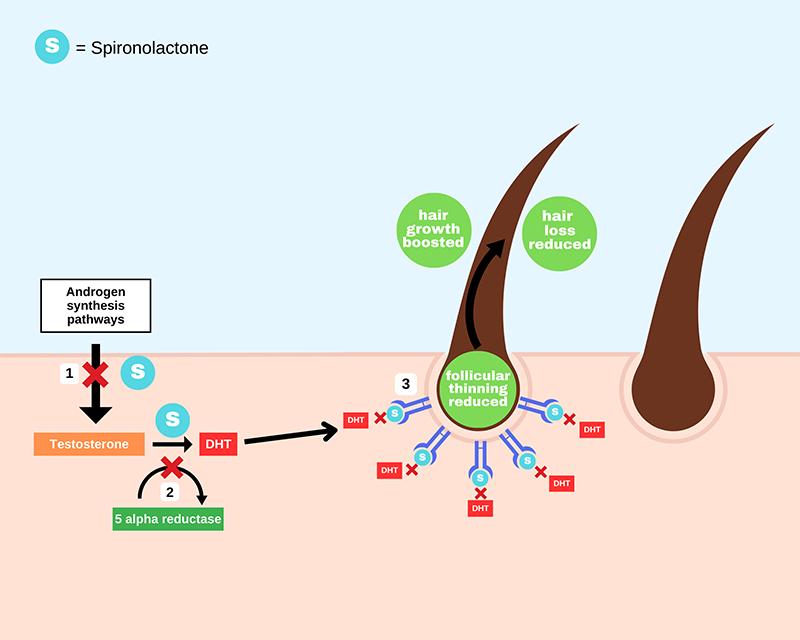
Figure 1: How spironolactone treats androgenetic alopecia
Reduced production of Testosterone and DHT
- Blocks the action of an enzyme (17-OH-Hydroxylase) necessary for testosterone production
- Blocks the action of 5-alpha reductase which stops testosterone from being converted to DH
Androgen receptor blocking
- Is able to bind to androgen receptors in areas such as the hair follicle. This prevents DHT from initiating the process of follicular miniaturization.
Androgenetic alopecia, also known as male-pattern baldness or female-pattern hair loss, is a common form of hair loss that affects both men and women. Generally, this time type of hair loss is caused by a combination of genetic and hormonal factors, primarily an excess of the hormone dihydrotestosterone (DHT). Hence ‘andro-’ (meaning related to androgen hormones) and ‘genetic’ (meaning related to genetic inheritance and activation of genes by our environment).
Spironolactone works by interfering with the hormonal component responsible for androgenetic hair loss in two ways. It works in a similar way to androgen receptor blockers such as RU-58841 and pyrilutamide as well as DHT blockers such as finasteride and dutasteride.
- Androgen receptor blocking
This is the main action of spironolactone for hair loss. DHT is a by-product of testosterone, and it binds to androgen receptors in hair follicles which leads to the activation of genes responsible for a process called ‘follicular miniaturization’.
Follicular miniaturization causes hairs to become thinner, brittle and eventually fall out. Because spironolactone has a structure which is similar to the naturally occurring sex hormone progesterone, it can interact with sex hormone receptors and block the action of androgens responsible for hair loss.3
When spironolactone binds with androgen receptors, it blocks the effects of androgens, including DHT. It does this by blocking the androgen receptors in hair follicles, preventing DHT from binding to them which can reduce the miniaturization of hair follicles and can promote regrowth and thickening.
- Reduction of testosterone and DHT production
Spironolactone reduces testosterone levels by inhibiting an enzyme called 17-hydroxylase, which is required for testosterone production. Spironolactone also shares an action with the DHT blockers, finasteride and dutasteride, inhibiting 5-alpha reductase, the enzyme responsible for the conversion of testosterone to the more potent DHT.4 This leads to a reduction in testosterone levels and a reduction of DHT levels in the scalp which can slow the process of follicular miniaturization.
However, hormones tend to work on a feedback loop and the reduced production of testosterone is compensated for by the increased production of two hormones, called Luteinizing hormone (LH) and Follicular stimulating hormone (FSH). These hormones help increase testosterone to normal levels and therefore normal dosing regimens are not associated with clinically significant reductions in testosterone levels.5
How to take spironolactone for hair loss.
Oral Spironolactone
Spironolactone is available in both oral and topical forms. Oral spironolactone is usually taken once (or twice daily if higher doses are needed). Taking spironolactone with a meal may help to reduce side effects such as nausea.
Topical spironolactone
Topical preparations are applied directly to the scalp and can even be combined with other hair loss treatments such as minoxidil. Topical preparations can come in the form of gels or solutions which are applied directly to the scalp. Topical spironolactone is still in the early stages of research, and more studies are needed to fully determine its effectiveness however it is thought to be associated with fewer side effects than oral spironolactone.1
Topical spironolactone should be applied to clean, dry hair and left for several hours to absorb into the scalp. Washing or blow-drying the hair after application may prevent the medication from working effectively.
Missed a dose?
If you forget to take a dose of spironolactone, take it as soon as you remember unless it’s close to the time for your next dose, in which case you should skip it and take your next usual dose. Never take two doses to make up for a missed one as this can increase the risk of side effects and cause imbalances in the salt levels in your body.
Spironolactone for hair loss – what does the evidence say?
The effectiveness of spironolactone for hair loss has been studied in several clinical trials. A recent systematic review concluded that spironolactone is an effective and safe therapy for androgenetic alopecia in male and female patients and can be combined with treatments such as minoxidil to improve efficacy. The review looked at 7 studies, comprising over 600 patients being treated for pattern hair loss and found that topical spironolactone was a safer treatment option appropriate for both male and female patients.1
Topical Spironolactone for hair loss
In one trial of over 60 patients (21 female and 39 male), 1% Spironolactone gel was associated with clinical improvement as assessed by scalp photography. These results were present in 80% of patients receiving topical spironolactone gel 1% alone for 12 months. This increased to 100% when patients were treated with a combination gel of minoxidil and spironolactone.6
A similar trial looking at 120 patients with pattern hair loss found that topical minoxidil 5% and spironolactone 5% were equally effective with an improvement in the features of hair loss, with both treatments individually and in combination demonstrating an increase in upright regrowing hairs at 12 weeks.7
Oral spironolactone for hair loss
In a 2015 trial, 75% of women receiving a mean dose of 100mg of spironolactone daily for female pattern hair loss reported stabilization or improvement in their condition.8 This agreed with an earlier trial which had found that 88% of women receiving oral anti-androgens such as spironolactone had improvement or stabilization of their hair loss.9
In a 2023 systematic review of multiple studies, including 200 patients across four studies, 81% of patients reported improvement in hair growth receiving spironolactone at doses ranging between 25mg and 200mg daily, with the vast majority from 80mg to 110mg.1
Overall, there is a good level of evidence to suggest that oral spironolactone is effective in treating pattern hair loss and androgenetic alopecia in women. Oral spironolactone is not suitable for treatment in male pattern hair loss due to side effects related to testosterone function. In one study, 10% of men receiving just 25mg per day of oral spironolactone for heart failure, experienced gynecomastia (increase in breast tissue) or breast pain.1 However, topical spironolactone is thought to be safe in both male and female patients.
It is important to note that spironolactone is not FDA-approved for the treatment of hair loss and is only available off-label when prescribed by an appropriately qualified physician.
What is the optimal dose of spironolactone for hair loss?
The optimal dose of spironolactone for hair loss varies depending on an individual’s age, gender, and overall health as well as the route of administration.
Oral
For women, the typical dose of spironolactone for hair loss is 100-200 mg per day.10 However, some studies have shown that lower doses, such as 50-75 mg per day, may also be effective.8
For men, the optimal dose of spironolactone for hair loss is not well established. This is because oral spironolactone is not a recommended treatment for pattern hair loss in men.11 Generally, men are prescribed lower doses of spironolactone compared to women due to the risk of side effects such as breast enlargement and decreased libido which are related to the effects on testosterone production and function.12
Topical
Dosage forms for topical spironolactone use include gels of 1% and solutions of 5%. These can be applied to the scalp twice daily.1
N.B. – It is important to note that the dosage of spironolactone should be carefully monitored by a healthcare provider, as high doses of spironolactone can cause serious side effects such as electrolyte imbalances and kidney damage.
What are the side effects of spironolactone?
Like all medications, spironolactone can cause side effects. The most common side effects of spironolactone include:
More than one in every 100 persons experience typical spironolactone side effects.
- Dizziness
- Nausea and vomiting
- Headache
- Fatigue, tiredness, or a lack of energy
- Diarrhea
Other less common but potentially serious side effects can include
- Leg or muscle cramps
- In addition, spironolactone can cause more serious side effects, such as:
- Electrolyte imbalances (low potassium or high potassium)
- Kidney damage
- Liver toxicity (yellowing of the eyes and skin)
- Gynecomastia (breast enlargement) in men
- Menstrual irregularities in women
It is important to talk to your provider before starting spironolactone to discuss the potential side effects and how to manage them.
Does topical spironolactone have fewer side effects than oral?
Topical spironolactone may have fewer side effects compared to oral spironolactone since it is applied directly to the scalp and does not enter the bloodstream at the same levels that oral spironolactone does. This means that the effects of spironolactone on androgen receptors and testosterone function could be limited to the scalp. However, large-scale research is needed to fully determine the safety and efficacy of topical spironolactone for hair loss.
How long does spironolactone for hair loss take to work?
Spironolactone does not work immediately for hair loss, so it’s important to continue using it, even if you don’t see results immediately.
It can take up to six months before you start seeing any results while in others it can take up to a year or longer.15
If after 6 months, you aren’t seeing any results, your physician may raise your dosage or recommend a different medicine to use alongside or instead of spironolactone based on your results.
If I stop taking spironolactone for hair loss – will I lose my hair?
If you stop taking spironolactone, you can experience a recurrence of hair loss. Because spironolactone acts by blocking the effects of androgens, stopping it means that androgens can again affect hair growth. The extent of hair loss may depend on how long you have been taking spironolactone, the dose, and other factors.
It is important to talk to your healthcare provider before discontinuing spironolactone or any medication, as they can provide guidance on how to safely stop the medication and manage any effects related to withdrawal.
Odor of spironolactone
Both topical and oral spironolactone has a distinct, sulfurous odor due to the presence of thiol groups in the compound and sulfur-containing metabolites13. This is likely to be more pronounced in the topical version. While some find the odor unpleasant, others report that it lessens quickly after application. The addition of fragrance or masking agents to the formulations of spironolactone products may help to improve the odor.
Stability of Topical and Oral Spironolactone
Spironolactone is generally considered to be stable when stored properly, with a shelf
However, the stability of spironolactone can be affected by factors such as temperature, pH, and exposure to light. Oral spironolactone is typically stored in a dry, cool place, while topical spironolactone should be kept in a dark, cool place to prevent degradation.
What is the half-life of spironolactone?
The half-life of spironolactone is 1.4 hours. This means that it takes about 1.4 hours for half of the drug to be eliminated from the body. However, the half-life of spironolactone’s active metabolite, canrenone has an average half-life of around 16 hours.14 This means that the effects of spironolactone can persist for some time even after the drug has been eliminated from the body.
Who can’t take spironolactone?
Certain people should avoid using spironolactone. To ensure your safety, inform your provider before beginning to use the medication if you:
- Have ever been allergic to spironolactone or any other medication
- Have Addison’s disease (a hormone imbalance that causes weakness, weight loss, and low blood pressure)
- If you have ever been diagnosed with kidney disease or renal issues or difficulty passing urine.
- Have ever been diagnosed as having excessive potassium levels in your blood
- Spironolactone should also be used with caution in individuals with liver disease, as it can cause liver toxicity.
Conclusion
In summary, spironolactone is a medication that has been used off-label for the treatment of hair loss, particularly in women with androgenetic alopecia. The evidence suggests that spironolactone is effective in reducing hair loss and improving hair density, although more research is needed to determine its optimal dosage and safety for men.
Spironolactone is available in both oral and topical forms, and the dosage should be carefully monitored by a healthcare provider to minimize the risk of side effects. Common side effects of spironolactone include dizziness, nausea, and headache, while more serious side effects include electrolyte imbalances and kidney damage.
It is important to talk to your doctor before starting spironolactone to discuss the potential benefits and risks and to determine whether spironolactone is the right treatment for you.
- Wang C, Du Y, Bi L, Lin X, Zhao M, Fan W. The Efficacy and Safety of Oral and Topical Spironolactone in Androgenetic Alopecia Treatment: A Systematic Review. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2023;16:603-12.
- Patibandla S, Heaton J, Kyaw H. Spironolactone. StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing
Copyright © 2022, StatPearls Publishing LLC.; 2022.
- Maron BA, Leopold JA. Aldosterone Receptor Antagonists. Circulation. 2010;121(7):934-9.
- Skinner MK. Encyclopedia of Reproduction: Elsevier Science; 2018.
- Jameson JL, De Groot LJ. Endocrinology: Adult and Pediatric: Elsevier Health Sciences; 2015.
- Abdel-Raouf H, Aly UF, Medhat W, Ahmed SS, Abdel-Aziz RTA. A novel topical combination of minoxidil and spironolactone for androgenetic alopecia: Clinical, histopathological, and physicochemical study. Dermatol Ther. 2021;34(1):e14678.
- Ammar AM, Elshahid AR, Abdel-Dayem HA, Mohamed AA, Elsaie ML. Dermoscopic evaluation of the efficacy of combination of topical spironolactone 5% and minoxidil 5% solutions in the treatment of androgenetic alopecia: A cross sectional-comparative study. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2022;21(11):5790-9.
- Rushton DH, Futterweit W, Kingsley D, Kingsley P, Norris MJ. Quantitative assessment of spironolactone treatment in women with diffuse androgen-dependent alopecia. Journal of the society of cosmetic chemists. 1990;42:317-25.
- Sinclair R, Wewerinke M, Jolley D. Treatment of female pattern hair loss with oral antiandrogens. British Journal of Dermatology. 2005;152(3):466-73.
- Fabbrocini G, Cantelli M, Masarà A, Annunziata MC, Marasca C, Cacciapuoti S. Female pattern hair loss: A clinical, pathophysiologic, and therapeutic review. Int J Womens Dermatol. 2018;4(4):203-11.
- Rathnayake D, Sinclair R. Innovative use of spironolactone as an antiandrogen in the treatment of female pattern hair loss. Dermatol Clin. 2010;28(3):611-8.
- Pitt B, Zannad F, Remme WJ, Cody R, Castaigne A, Perez A, et al. The Effect of Spironolactone on Morbidity and Mortality in Patients with Severe Heart Failure. New England Journal of Medicine. 1999;341(10):709-17.
- Gardiner P, Schrode K, Quinlan D, Martin BK, Boreham DR, Rogers MS, et al. Spironolactone metabolism: steady-state serum levels of the sulfur-containing metabolites. J Clin Pharmacol. 1989;29(4):342-7.
- Carone L, Oxberry SG, Twycross R, Charlesworth S, Mihalyo M, Wilcock A. Spironolactone. J Pain Symptom Manage. 2017;53(2):288-92.
- https://www.practiceupdate.com/content/oral-spironolactone-is-safe-and-effective-for-androgenic-alopecia/121841